 Monday, 08 August 2005
I am going to discuss code generation over the next few posts for a couple of reasons. One is that it is fundamental to the process of software industrialization and second, most programmers, that I know of anyway, dont like code generators, for a variety of reasons.
Maybe I should step back and give you my definition of what code generation means to me. I am pretty sure we all have different ideas as to what this means. Again, I will draw upon our analogy of AutoCAD. Lets say I produce a drawing of a piston used for a race engine. Once I have completed the drawing, I can then save the entire definition of that race piston in a universal file (i.e. DXF) format. I can then take that piston file definition and feed it into a Computer Numerical Control (CNC) milling machine, which will produce (in our terms, code generate) the output, virtually 100% complete, save for a few finishing touches (i.e. polishing).
Thats the key. I am required to produce a drawing that is 100% complete up front (i.e. design) before I can mill out the piston for my race engine. When do we specify (i.e. design) anything that is 100% complete up front in the software world? If I can design a software part or solution 100% up front, then I can code generate the solution, given the proper tools.
As a programmer, I would rather build the (code generator) tool that is going to produce the solution rather than the solution itself. Why? Because, in my experience, I know I am going to have to do it over and over again, just to get it right.
Traditionally, I would incrementally iterate my way through the solution code several dozen (or even hundreds) of times which will ensure I have a POS by the time it is ready to deploy into production.
So give me a design tool that allows me to draw and define what is supposed to be built (saved in a universal file format) and then I can build a code generator to read the design file and produce the solution output. The effort is in the design and code generator, not in the solution code. It takes minutes to code generate a solution - every time.
Hey, I like to code as much as the next programmer. But I am getting too old and tired and cant stay up to 4am for a week in a row when it comes down to crunch time for the final push to deliver I dont know what to the client. If I am going to code anything, it is going to be a code generator.
If I build a code generator to read a file format that contains the definition (i.e. design) of a solution, then I can make changes to the design, just like when I want to change the shape or dimensions of the piston. And if I am really smart, I would have a library of piston designs that I have accumulated over time, along with other reusable design pieces or parts (read: design patterns).
We have several excellent books that document design patterns for virtually everything in software, including the infamous (Gamma et all), EAI design patterns, and in fact, if you type in software design patterns in Google, you get 18,900 hits. So why dont we have code generators that take these design patterns as input? Why not create a standardized library of design patterns that any IDE can read and produce the required output in your language of choice? Oops, there is that word again, standard.
Next post will delve deeper into code generators.
 Friday, 05 August 2005
Barrys and my invention, and the specific implementation of that invention, is so new and abstract, that it is a real challenge to bring the software to market. As John Walker, inventor of AutoCAD has said, we need to find lunatic early adopters to try the software out and evolve quickly from there.
As discussed earlier, our software world is incredibly complex and highly abstract, so much so, it is virtually (no pun intended) impossible to describe our invention to business people and even to technical people in our own specific area of our industry. Why is that? There have been many reasons given over the last several posts, but it comes down to our invention is ahead of its time. I believe this is an inherent characteristic of any invention, because an invention is just that, it is brand new and requires people to think in ways that they never have thought of before. What makes our invention even harder to understand is that it works in the virtual world of software which is already a complete mystery to most people.
Think of it this way, we invented a standard way to design (i.e. draw and define) application integrations of any size and complexity. The resulting output definition can be read by other drawing tools and therefore can be reused to replicate or use as a template for other companies application integrations that have similar business scenarios. In other words, the drawings form a library of business process integrations that can be reused by anyone, much like the way AutoCAD has a library of pre-built designs that can also be leveraged by anyone. This, in my mind, is advancing the industrialization of software.
We also invented an intelligent messaging definition that can be used by any middleware engine, in our case we are using BizTalks middleware engine. However, our intelligent message is a complete abstraction away from any middleware engine implementation. This means that other middleware engines can use the same standard file definition for business process execution.
And thats the key to our invention, much like AutoCADs invention of the DXF universal file format which "is probably one of the most widely supported vector formats in the world today". We have invented design-time and run-time XML schema definitions that any drawing tool (design time) and middleware engine (run-time) can use as both definitions contain everything required to define and execute any business process integration scenario totally independent of programming languages, operating systems, middleware engines or any implementation details whatsoever. In my opinion, this is raising the level of abstraction to a new level our software development world has not yet seen. You heard it here first 
How would other middleware engine manufacturers use our invention? For example, Sun acquired SeeBeyond, which is a middleware engine, therefore Sun could use our invention to not only automate the design and code generation of application integrations for SeeBeyond, but also, and more importantly, build a library of reusable business process integrations for their entire application suite of software products.
Microsoft Indigo is another middleware engine that could benefit from our invention. Microsoft could use BRIDGEWERX as part of their Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) strategy. SOA is the latest TLA in our industry.
You would think with the amount of words written in these posts that this was turning into a book. It is! I decided in January of this year to write a book titled, The Industrialization of Software (shameless plug) to help educate people (and inventors alike) about our strange software world and even more bizarre business world of software. It chronicles my 4 years as President of 5by5Software and details most of the topics you have read over the last several posts that Shane Schick has been kind enough to post on ITBusiness.ca
As I see it, we are in a software revolution where the last 4 years of IT has been the worst in the history of our industry. Businesses have revolted against the software world largely because of our abysmal track record of delivering quality software. Now the general public (with AntiSpyware, SPAM, etc.) have entered the fray. For those of you that use software in your daily life, you have the power to make (demand!) the necessary changes in our software industry to bring us out of the dark ages and force us into the industrialization of software.
 Thursday, 04 August 2005
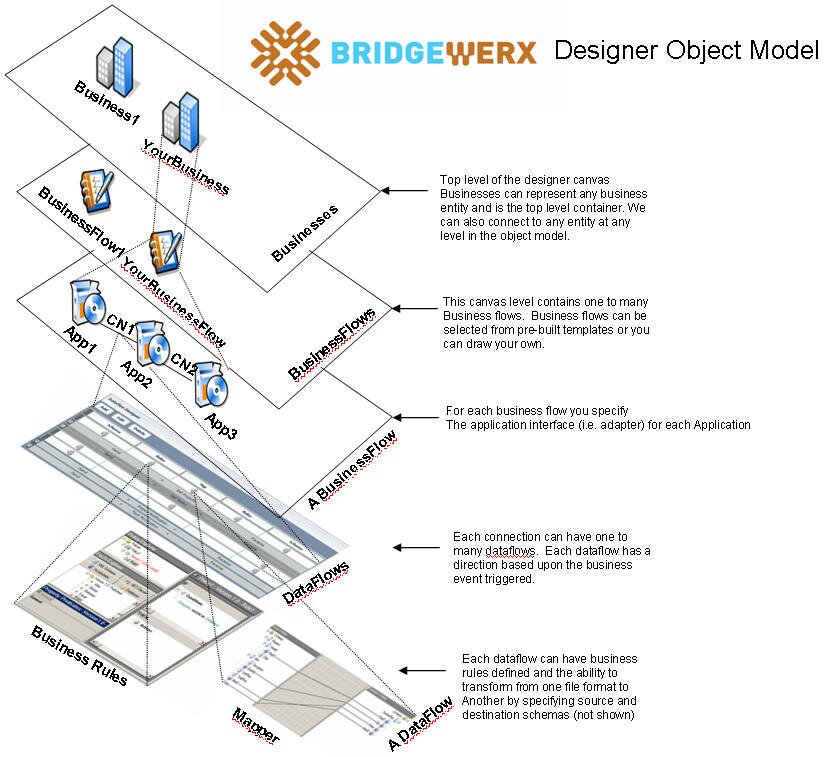
Have a look at this object model. This is our modeling design pattern that Barry and I figured out after designing and constructing 25 application integration solutions over a 4 year time frame. This design pattern raises the level of abstraction for designing and constructing application integrations into a fully automated process that is predictable and repeatable.
How does it work? We have taken our design pattern and implemented it as a drawing/modeling tool, much like AutoCAD, where you can draw your application integration scenarios on a canvas. The modeling tool produces a full-fidelity or complete design specification output in which a code generator can read the completed specification and automatically produce (i.e. code generate) the solution, wrapped as an installation package, much like using an installation wizard to install a program on your computer.
At run-time, there are several administrative, operational and monitoring tools that are provided to manage the solution that are installed on a pre-configured technology stack, including a middleware engine. In fact, everything can be pre-installed onto a DELL server and delivered as a complete integration appliance.
Here is another view of the object model as represented by the layers or levels in our modeling/drawing tool. This is how we visualize size and complexity. Just like how AutoCAD has many levels of detail, we do too. We can view the upper most level to see the big picture (which may contain dozens of application integration scenarios across several business entities) and yet drill down, level by level, to the lowest level of detail of an individual data element that is being mapped for example. We can see the entire size and complexity of the business process problem being solved.
Another key to our invention is the Intelligent Messaging format. The intelligent messaging format is intended to be used as a standard wrapper for all messages flowing through an integration at run-time. The actual message content (i.e. data) is contained within the envelope as a payload. The envelope also contains a number of other fields used to control its flow through the business process and to record the route and activities undertaken during that process.
The use of a standard schema allows a higher degree of abstraction within a business process as this standard schema contains (i.e. encapsulates) all business process rules and state information necessary to execute the business process integration without any knowledge of the rest of the system and vice versa (i.e. fully abstracted). The word standard is very important in our software world as there are few standards. We invented a standard messaging format for executing application integrations in addition to a standard object model (i.e. drawing tool) that allows business analysts to fully design and describe application integrations in hours/weeks that are code generated and installed in minutes.
You would think an invention like this would help, in some small way, industrialize our software world like AutoCAD did for the engineering design world in the early 80s. However, as with most inventions, including AutoCAD, getting to market is an entirely different story which I will describe in tomorrows post.
 Wednesday, 03 August 2005
David Frankel wrote an excellent article called, Software Industrialization and the New IT, that describes what software abstractions are and why we want to raise the level. First we started with 1s and 0s, which is ultimately what the computer understands, but as David points out, there has to be a better way. There is, it was assembly language, ha ha, then third generation languages (3GLs) and then Model Driven Architecture (MDA) which represents the highest level of abstraction today. As described in David's article, we continue to push the envelope with the next level of abstraction called, Computer-Assisted Business Process Management (CA-BPM) in which Barry Varga and I have invented one of these for the application integration world.
Ultimately, we want a drawing/modeling tool that allows a business analyst or a person that is not necessarily a programmer, to draw and describe the software to be built. Since we are talking a virtual world here, the construction process (i.e. writing the code) can be fully automated using code generators that know how to read the output format of the drawing tool and code generate the solution to run on a target business process engine or server platform. Therefore turning our incredibly labor intensive and error prone software development process into one that is predictable and repeatable.
Why dont these CA-BPM tools exist today? There are several reasons for this, as discussed in earlier posts, but mostly due to the newness of our industry compared to other engineering disciplines. I would like to introduce you to a CA-BPM tool that can fully describe size and complexity in the application integration domain.
The need for application integration arose from executing business processes across software applications because no one application can do it all (unless it is SAP, right George  For example, when you order your computer from DELL, there are several business processes that are executed. Placing the order, credit card transaction, procurement, inventory and order management, scheduling, back-orders, assembly, test, burn-in and finally, delivery. I may be missing a few steps, but you get the idea. It may come as a surprise that there could be a dozen computer applications/programs used in this end-to-end business process, with each application communicating data to one or more applications. Or at least trying to communicate data, which is where all the integration issues are.
Application integration is considerably more complex, abstract and error prone then straight application development. The middleware engine is what controls message flow (i.e. data) and orchestrates a business process (or multiple processes) between these applications. Application integration development is very difficult to understand as it is akin to trying to connect wires together in a wiring closest that has thousands of colored coded wires, yet there is no wiring diagram with numbers or labels or an obvious meaning to the color codes. This leads to a process of discovery that is long, painful, expensive, mostly trial and error and with an end result that may be less than the 20% success rate discussed in the CHAOS Study.
However, over time, eventually you figure it out and if you do it enough times you get good at it and the more you do, the more you see the patterns on how it is done and how to do it better each time. This is how we evolved our invention, which after 25 application integration projects over a period of 4 years, Barry Varga and I arrived at BRIDGEWERX. And by all accounts, it appears we were first to market with this invention.
Tomorrow we reveal our design pattern to show how we can model any application integration scenario that scales to any size or complexity.
 Tuesday, 02 August 2005
Today, we are on a journey of the industrialization of software much the same way when Autodesk invented AutoCAD in 1982 and introduced it to the engineering design and manufacturing production world. AutoCAD offered, for the first time, a full-fidelity drawing tool that enabled a predictable and repeatable way to produce engineering diagrams that could be saved electronically in a (publicly accessible) universal file format to be used by all sorts of other CAD/CAM devices. A standard was born. In my opinion, AutoCADs virtual drawing world has done more for the engineering design and manufacturing world then any other invention in the last 20 years. Without it, we would still be forging hammers by hand at a rate of one a month and cost several thousands of dollars a piece to produce.
The same revolution is now taking place over 20 years later for the software design and code production world. The only people that really know about it are software programmers from various tool vendors around the world. Programmers are realizing that the days of hand crafting ever increasing complex software solutions are becoming too costly and taking too long in our internet time business world. I predict in the next 5 years we are going to see the business world using software that is heading up the knee of the exponential curve and offer business services through software automation that are going to further increase the speed of which business is performed compared to today on a scale that is unfathomable. Just as unfathomable as the railroad once was. Just as unfathomable as electricity once was.
The software industry need tools that can visualize the size and complexity of the software structures to be constructed much like how the (traditional) building industry uses architectural blueprints to visualize the design of building structures and yet, are detailed enough to cover all aspects of the building to be constructed. Not only will this give some sort of continuity to the world of software development, but will help non-technical people understand the (equivalent) difference between constructing their 3 bedroom bungalow house and the Empire State building. Even a lay person with no level of expertise can visualize by looking at the blueprints and generally comprehend one is much bigger and more complex than the other.
Right now in the software industry we have no universal way of showing size and complexity differences even amongst the programming community. The current state of the art is still so low level and specialized, that most programmers look at these crude architectural drawings and cant infer any meaning as to what is to be built, aside from understanding what the size and complexity is. Sure we have software modeling languages like the Unified Modeling Language (UML) and the newly introduced Domain Specific Language (DSL), but these tools and languages are still very low level compared to a buildings architectural blueprint.
I am not trivializing these language inventions, in fact, they have done a world of good for the software world. However, we need to raise the level of abstraction using better modeling tools and languages so we can get ourselves out of the dark ages and into the industrialization age.
Raising the level of abstraction is the topic of my next post.
 Friday, 29 July 2005
Ok, we IT people in the software world have been known to take ourselves way too seriously (including myself) on occasion (how about all the time) so today we are going to have some nonsense. The nonsense I am talking about is my washing machine. Now my long time friend and co-founder of 5by5Software, Barry Varga, has asked me what I was doing around a washing machine in the first place. Well, I was fixing it for my lovely wife, Lesley. Yah, thats the ticket.
Remember the annoying beep beep beep firmware problem? Well, its back. It seems that Lesley has pressed some magical key combination that caused the infernal machine to resume beeping, three beeps on the minute, every minute when the machine says its done. Someone in the house has to physically go over to the machine and manually turn it off. Sledgehammer anyone?
But there is more, and here is where the annoying crosses the boundary into the stupefying. Lesley likes to add things to the wash, whilst the washer is washing. This according to her is common practice. So she presses the pause button (no kidding, there is a pause button) and tries to open the door. You guessed it, the door wont open. Her words were, why wont the machine do what I want it to do? I used to do this with my old washer (not software controlled) and not only could I stop and add items at any time, I can even restart and the washer would already know what level the water was at and not add any more. I would have liked to tell her that once we purchased a computer controlled machine that she is no longer in control, but I am sure she does not want to hear that  In the end, this means I get enlisted to fix it.
First, I do the unthinkable and consult the 27 page manual first (told ya, I am a geek). Searching through the manual I come across the following statement, Adding laundry is not possible because the door is locked for safety reasons. The very next line says, Laundry may be added after pressing the Start/Stop button. Huh? In fact, in several places these contradictory statements are made. There is some (stupid computer) trick to make it work because we still cant open the door, even after pausing the machine and even after following the procedure(s) in the manual. Obviously, as I told Lesley, we must call the manufacturer and request a secret decoder ring to figure out the magic computer logic sequence to unlock the door.
Lesley has something to say to the designers of this machine. As far as she is concerned, the old washer lets you do this and the new one doesnt. From her perspective, the new washer is a poor design as it does not meet her requirements and she is frustrated that the machine and the instruction manual are so complicated, that she gives up. Someone at the new washer manufacturer has played a stupid computer trick on her.
And thats the point. Something as simple as a computer controlled washing machine appears to be too complicated to get right in the way of features and user interface design. How hard can this be? What does that say about software programs that are 100 or 1000 times the size and complexity?
Next week we are continuing with the industrialization of software where the topic will be lessons in abstractions using modeling tools.
 Thursday, 28 July 2005
Why do most people today view software as a commodity product when nothing could be farther from the truth? As a software developer type, I could blame it on marketing, but that is not the whole story.
Software is to most people, completely intangible. That is to say nebulous. The laws of physics seemingly dont apply to our world of software. Software does not have a physical shape or a form that one can readily see or touch, other than on a computer screen. And even on the computer screen, you do not see the actual size or complexity of the software because it isnt all on one screen. In fact, you have no idea how many screens there are. And even if you knew how many screens there were, it still gives you no indication to the size and complexity of the software program. But once the computer is turned off, where did the software go? Poof! Its just like being at a magic show (and for some vendors of software, it truly is a magic show 
Hundreds of billions of dollars are spent on software development, it permeates into almost everyones daily life, but it mostly does not occupy a physical space like the Empire state building for example. The Empire State building cost $43 million dollars to design and construct, required 3600 people and 7 million person hours of effort and took one and half years to complete. Most people can understand why once they see the size and complexity of the Empire State building.
However, in the software world, we are routinely asked to build such structures, with respect to equivalent size and complexity, with a nothing more than a few hundred thousand dollars (at best) with a handful of people, whose programming skills vary wildly, (a topic for a future post), and guess what, can you deliver that software to us next week? Ridiculous, yet it happens all the time. It is still happening today. Status quo continues.
Until we have a way of describing software size and complexity in the form of an architectural drawing or structural blueprint, that people can understand, we will continue to perpetuate software development as a massively labor intensive, non-predictable and non-repeatable, error prone process and remain in the pre-industrialization world forever.
Next week we will look at a new way of describing size and complexity using a modeling tool that produces architectural blueprints (and code generated solutions as it turns out).
However, tomorrow is Friday and time for Stupid Computer Tricks!
 Wednesday, 27 July 2005
It is no wonder to me why our software industry is in serious trouble. FBI officials said they hope to award a contract by the year's end for a complex new software program to replace a failed project that was canceled this year at a cost of more than $100 million to taxpayers.
Closer to home, the Canadian government has spent over $2 billion (yes, $2 billion!) on a gun registry that is nothing more than a giant database for storing information about legal owners of guns who have volunteered to register their weapons. But $2 billion dollars? To coin a Dave Barry phrase, I am not making this stuff up. It really happened.
The software that controls the baggage handling at the Denver airport where, due to a bug in the software, it was costing the airport $1.1 million dollars of lost operational cost per day! At the time this was occurring, there was no predicted end in sight.
Finally, have a look at The CHAOS Study which reveals mind boggling statistics on software development failures. The report summarizes that in 1995, the U.S. spends $250 billion per year on information technology for 175,000 software projects. 31% of those projects were canceled before completion. 53% of those projects cost 189% of original estimates. $81 billion was spent on canceled projects. Only 16% of software projects were complete on-time and on-budget. 16% wow!
Some of you may point out that this report is 10 years old. I can tell from my own experience, and others, not much has changed since then. In fact, an updated report verifies this.
For the experienced software developer, this does not come as a surprise. Disheartening yes, surprising, not really we live it - everyday. The CHAOS Report states that the top three causes for these failures are the lack of user input, incomplete requirements and changing requirements. No surprise here either, however, I would like to offer up what I would call the root cause of these failures, that is not categorized in the report, which is totally underestimating the size and complexity of any software development effort.
Software development is an incredibly complex, highly skilled, maximally labor intensive process, probably more so then any other professional human endeavor. Software design and programming is so complex and error prone that it is totally underestimated by everyone, including the majority of software programmers who are closest to truly understanding this size and complexity issue. Further, the people that we are trying to develop the software for have no idea about size or complexity or how software is designed, built or even how it works. It is a complete mystery to almost everyone.
Tomorrow we are going to delve deep into this size and complexity issue.
 Tuesday, 26 July 2005
In my discussion on certifying IT Architects, I came across this quote, But much of the work that architects do today is really an art form, not a certifiable set of practices, said James Barry, vice president of development for payroll and human resources applications at Automatic Data Processing Inc. (ADP) in Roseland, N.J. "The written communication and how they present their architecture would be mainly what we would look for in an architectural certification -- not the methodology that determines what to build," he said. "That would come from experience, not certification."
I am really beginning to wonder if we will ever get out of the dark ages in the software development world. With all due respect to Mr. Barry, I must admit I am dumbfounded by his comments. Art form? How they present their architecture? Lets look up the definition of Architect, One who designs and supervises the construction of buildings or other large structures I would say that definition applies to an IT architect as well except that our buildings are software structures. The art in architecture is around the look and feel of the structure, much like that of the user interface in a software structure.
However, in my experience, the look and feel represents less than 10% or even 5% of what an IT Architect does. We spend most of our time designing software structures so that they do not fall down! We design software blueprints much like a building architect would design building blueprints for any size structure. We design and construct software architectures indeed on a best set of practices, like Grady Boochs executable architecture which is an industry best practice and has been for over 10 years. A comment from a reader of my previous post (thanks Brian Di Croce!) mentioned that there is a Software Engineering Body of Knowledge available, called SWEBOK. Perfect!
In fact, it is indeed the methodology (I prefer practice or body of knowledge) that makes an IT Architect successful in the way that s/he can predict and repeat successes in an industry that isnt too successful. Thats the premise behind the Software Engineering Institutes Capability Maturity Model. You follow a prescriptive approach for increasing the maturity of your software development process by using sound engineering principles for developing software. The mantra is, the quality of a software system is highly influenced by the quality of the processes used to develop and maintain it.
This is much in the same way a building architect follows, well known, defined processes for designing and constructing buildings. Patrick MacLachlan, one of my co-workers at Burntsand is a real Architect. I asked him what it took to get his Architects degree. Patrick said it takes 8 years minimum and on average, 10 to 12 years!
Look at what Patrick had to do to obtain his Architects degree. How can we take certifying our IT Architects seriously when there is no prescribed body of knowledge, no exams and takes 3 to 6 months to certify? What a sorry state our software industry is in. This sorry state will be the topic of my next post.
 Monday, 25 July 2005
In my last post, I discussed the issues around using the title Software Engineer and how our educational system (i.e. Computer Science programs) needs to get into the software engineering game. While perusing about on this topic, I come across a posting on Grady Boochs site called, Certification of IT Architects.
Reading the Open Groups faqs, I came across this statement, 2.2 Will there be tests required to obtain the IT Architect certification? Since there is no prescribed body of knowledge for the program, there is no test. Instead we will assess candidates experience and skills against the requirements of the program by evaluating their written applications and by a Certification Board interview.
The faqs go on to say how long it will take to obtain certification (3 to 6 months) and how much it costs ($1250 for the assessment plus $175 per annum to remain certified plus recertification every 3 years).
Now, I am all for industrializing our software world, but something bothers me here. It is the statement that there is no prescribed body of knowledge and therefore no test. No prescribed body of knowledge for an IT Architect? Come on, of course there is. Any seasoned IT Architect can pretty much tell you what the body of knowledge is required to be successful at the job. It is the same body of knowledge that has been required since the first commercial software project was written some 40 years ago.
It goes something like this: requirements, design, code and test. Over and over again. In fact, it has never changed, other than the fancy marketing names that have been attached to this process over the years. Oh yes, you need some project management skills that you can find in the Project Management Book of Knowledge (been around for 20 years). Specifically, I would also suggest Grady Boochs excellent book on (been around for 10 years) as a body of knowledge. You will need some body of knowledge on the process of quality as well, the Software Engineering Institute, has several bodies of knowledge on this subject area, including software engineering in general. The SEI has been around for over 20 years.
10 years ago, I took a post-graduate, 2 year certificate program, called, Software Engineering Management at the University of Calgary taught by Karl Williams on behalf of Motorola University. I can tell you there was a body of knowledge because I had to write 17 exams over those two years to prove I knew what it was.
With respect to being a certified IT Architect, I am disappointed that our software industry would let an organization be accredited to issue certificates without any requirements for a prescribed body of knowledge and no written exams. How is this advancing the industrialization of software development?
© Copyright 2008 Mitch Barnett - Software Industrialization is the computerization of software design and function.
newtelligence dasBlog 2.2.8279.16125 Theme design by Bryan Bell
 | Page rendered at Tuesday, 09 December 2008 23:16:17 (Pacific Standard Time, UTC-08:00)
|
On this page....
Search
Categories
Navigation
Sign In
|